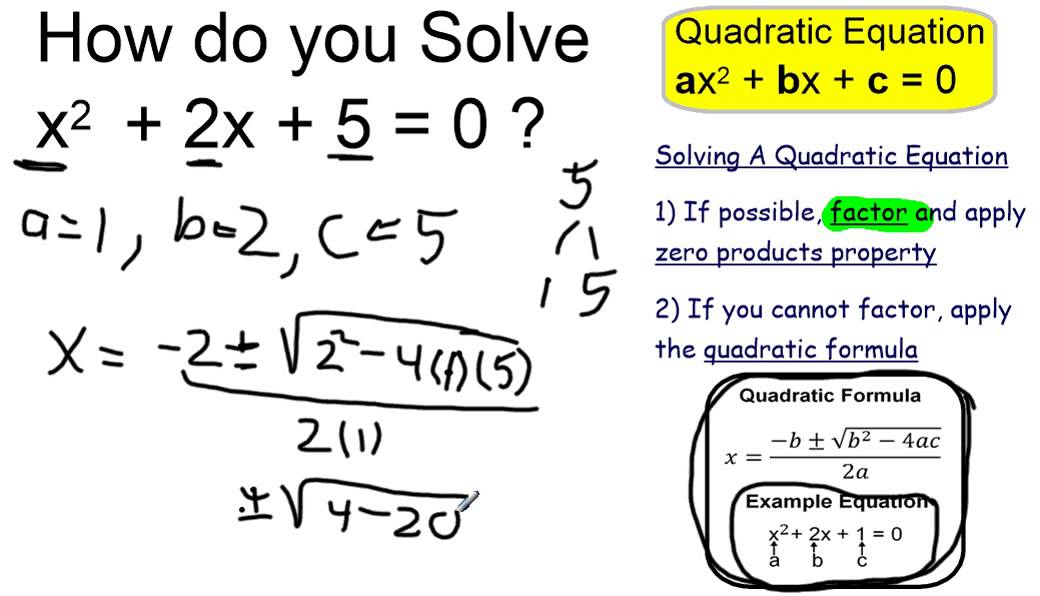
| 1 Angstrom = |
|---|
| 1 x 10-8 centimeters |
| 5.4681 x 10-11 fathoms |
| 3.2808 x 10-10 feet |
| 4.9710 x 10-13 furlongs |
| 3.9370 x 10-9 inches |
| 1 x 10-13 kilometers |
| 1 x 10-10 meters |
| 0.0001 microns |
| 6.2137 x 10-14 miles |
| 1 x 10-7 millimeters |
| 0.1 nanometers |
| 5.3996 x 10-14 nautical miles |
| 100 picometers |
| 1.0936 x 10-10 yards |
| 1 Centimeter = |
|---|
| 100,000,000 angstroms |
| 0.0054681 fathoms |
| 0.032808 feet |
| 4.9710 x 10-5 furlongs |
| 0.39370 inches |
| 1 x 10-5 kilometers |
| 0.01 meters |
| 10,000 microns |
| 6.2137 x 10-6 miles |
| 10 millimeters |
| 10,000,000 nanometers |
| 5.3996 x 10-6 nautical miles |
| 1 x 1010 picometers |
| 0.010936 yards |
| 1 Fathom = |
|---|
| 1.8288 x 1010 angstroms |
| 182.88 centimeters |
| 6 feet |
| 0.0090909 furlongs |
| 72 inches |
| 0.0018288 kilometers |
| 1.8288 meters |
| 1,828,800 microns |
| 0.0011364 miles |
| 1,828.8 millimeters |
| 1.8288 x 109 nanometers |
| 0.00098747 nautical miles |
| 1.8288 x 1012 picometers |
| 2 yards |
| 1 Foot = |
|---|
| 3.048 x 109 angstroms |
| 30.48 centimeters |
| 0.16667 fathoms |
| 0.0015152 furlongs |
| 12 inches |
| 0.0003048 kilometers |
| 0.3048 meters |
| 304,800 microns |
| 0.00018939 miles |
| 304.8 millimeters |
| 304,800,000 nanometers |
| 0.00016458 nautical miles |
| 3.048 x 1011 picometers |
| 0.33333 yards |
| 1 Furlong = |
|---|
| 2.0117 x 1012 angstroms |
| 20,117 centimeters |
| 110 fathoms |
| 660 feet |
| 7,920 inches |
| 0.20117 kilometers |
| 201.17 meters |
| 201,168,000 microns |
| 0.125 miles |
| 201,168 millimeters |
| 2.0117 x 1011 nanometers |
| 0.10862 nautical miles |
| 2.0117 x 1014 picometers |
| 220 yards |
| 1 Inch = |
|---|
| 254,000,000 angstroms |
| 2.54 centimeters |
| 0.013889 fathoms |
| 0.083333 feet |
| 0.00012626 furlongs |
| 2.54 x 10-5 kilometers |
| 0.0254 meters |
| 25,400 microns |
| 1.5783 x 10-5 miles |
| 25.4 millimeters |
| 25,400,000 nanometers |
| 1.3715 x 10-5 nautical miles |
| 2.54 x 1010 picometers |
| 0.027778 yards |
| 1 Kilometer = |
|---|
| 1 x 1013 angstroms |
| 100,000 centimeters |
| 546.81 fathoms |
| 3,280.8 feet |
| 4.9710 furlongs |
| 39,370 inches |
| 1,000 meters |
| 1 x 109 microns |
| 0.62137 miles |
| 1,000,000 millimeters |
| 1 x 1012 nanometers |
| 0.53996 nautical miles |
| 1 x 1015 picometers |
| 1,093.6 yards |
| 1 Meter = |
|---|
| 1 x 1010 angstroms |
| 100 centimeters |
| 0.54681 fathoms |
| 3.2808 feet |
| 0.0049710 furlongs |
| 39.370 inches |
| 0.001 kilometers |
| 1,000,000 microns |
| 0.00062137 miles |
| 1,000 millimeters |
| 1 x 109 nanometers |
| 0.00053996 nautical miles |
| 1 x 1012 picometers |
| 1.0936 yards |
| 1 Micron = |
|---|
| 10,000 angstroms |
| 0.0001 centimeters |
| 5.4681 x 10-7 fathoms |
| 3.2808 x 10-6 feet |
| 4.9710 x 10-9 furlongs |
| 3.9370 x 10-5 inches |
| 1 x 10-9 kilometers |
| 1 x 10-6 meters |
| 6.2137 x 10-10 miles |
| 0.001 millimeters |
| 1,000 nanometers |
| 5.3996 x 10-10 nautical miles |
| 1,000,000 picometers |
| 1.0936 x 10-6 yards |
| 1 Mile = |
|---|
| 1.6093 x 1013 angstroms |
| 160,934 centimeters |
| 880 fathoms |
| 5,280 feet |
| 8 furlongs |
| 63,360 inches |
| 1.6093 kilometers |
| 1,609.3 meters |
| 1.6093 x 109 microns |
| 1,609,344 millimeters |
| 1.6093 x 1012 nanometers |
| 0.86898 nautical miles |
| 1.6093 x 1015 picometers |
| 1,760 yards |
| 1 Millimeter = |
|---|
| 10,000,000 angstroms |
| 0.1 centimeters |
| 0.00054681 fathoms |
| 0.0032808 feet |
| 4.9710 x 10-6 furlongs |
| 0.039370 inches |
| 1 x 10-6 kilometers |
| 0.001 meters |
| 1,000 microns |
| 6.2137 x 10-7 miles |
| 1,000,000 nanometers |
| 5.3996 x 10-7 nautical miles |
| 1 x 109 picometers |
| 0.0010936 yards |
| 1 Nanometer = |
|---|
| 10 angstroms |
| 1 x 10-7 centimeters |
| 5.4681 x 10-10 fathoms |
| 3.2808 x 10-9 feet |
| 4.9710 x 10-12 furlongs |
| 3.9370 x 10-8 inches |
| 1 x 10-12 kilometers |
| 1 x 10-9 meters |
| 0.001 microns |
| 6.2137 x 10-13 miles |
| 1 x 10-6 millimeters |
| 5.3996 x 10-13 nautical miles |
| 1,000 picometers |
| 1.0936 x 10-9 yards |
| 1 Nautical Mile = |
|---|
| 1.852 x 1013 angstroms |
| 185,200 centimeters |
| 1,012.7 fathoms |
| 6,076.1 feet |
| 9.2062 furlongs |
| 72,913 inches |
| 1.852 kilometers |
| 1,852 meters |
| 1.852 x 109 microns |
| 1.1508 miles |
| 1,852,000 millimeters |
| 1.852 x 1012 nanometers |
| 1.852 x 1015 picometers |
| 2,025.4 yards |
| 1 Picometer = |
|---|
| 0.01 angstroms |
| 1 x 10-10 centimeters |
| 5.4681 x 10-13 fathoms |
| 3.2808 x 10-12 feet |
| 4.9710 x 10-15 furlongs |
| 3.9370 x 10-11 inches |
| 1 x 10-15 kilometers |
| 1 x 10-12 meters |
| 1 x 10-6 microns |
| 6.2137 x 10-16 miles |
| 1 x 10-9 millimeters |
| 0.001 nanometers |
| 5.3996 x 10-16 nautical miles |
| 1.0936 x 10-12 yards |
| 1 Yard = |
|---|
| 9.144 x 109 angstroms |
| 91.44 centimeters |
| 0.5 fathoms |
| 3 feet |
| 0.0045455 furlongs |
| 36 inches |
| 0.0009144 kilometers |
| 0.9144 meters |
| 914,400 microns |
| 0.00056818 miles |
| 914.4 millimeters |
| 914,400,000 nanometers |
| 0.00049374 nautical miles |
| 9.144 x 1011 picometers |
Combined Rotation and Translation using 4x4 matrix.
A 4x4 matrix can represent all affine transformations (including translation, rotation around origin, reflection, glides, scale from origin contraction and expansion, shear, dilation, spiral similarities). On this page we are mostly interested in representing 'proper' isometries, that is, translation with rotation.
We can combine two successive rotations about the origin by multiplying their matrices:
| r00 | r01 | r02 | | r10 | r11 | r12 | | r20 | r21 | r22 |
| = | | ra00 | ra01 | ra02 | | ra10 | ra11 | ra12 | | ra20 | ra21 | ra22 |
| * | | rb00 | rb01 | rb02 | | rb10 | rb11 | rb12 | | rb20 | rb21 | rb22 |
|
Pikka 2 0 4 X 4.5
We can combine two successive translations by adding their vectors:
So how can we represent both rotation and translation in one transform matrix?
To do this we put the rotation matrix in columns and rows 0,1 and 2, we put the translation vector in the right column, the bottom row is 0,0,0,1.
Pikka 2 0 4 X 40
| r00 | r01 | r02 | t0 |
| r10 | r11 | r12 | t1 |
| r20 | r21 | r22 | t2 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Disk map 2 5 x 8. We can use this matrix to transform points or vectors. If we want to transform vectors then we represent it with the 4th row set to zero:
When multiplied by the above matrix the vector will be rotated only and not effected by the translation value. If however we want to transform points then we represent it with the 4th row set to one:
This will both rotate and transform the point. Pixelmator 3 0 – powerful layer based image editor.
To combine subsequent transforms we multiply the 4x4 matrices together. How is this multiplication of matrices equivalent to addition of the translation vectors?
One way to understand this is to realise that we are using projective geometry (see box on right).
Pikka 2 0 4 X 4 Engine Compartment
An alternative way to show this is more of a brute force method; we can multiply two matrices representing pure translation and confirm that the translations get added: